Steam turbine generators are a crucial component of many power plants around the world. They play a vital role in converting thermal energy into electrical energy efficiently. Understanding how these generators work can provide valuable insight into the process of generating electricity on a large scale.
Contents
- 1 Introduction to Steam Turbine Generators
- 2 Working Principle of Steam Turbine Generators
- 3 Components of a Steam Turbine Generator
- 4 Efficiency and Output of Steam Turbine Generators
- 5 Types of Steam Turbine Generators
- 6 Applications of Steam Turbine Generators
- 7 Maintenance and Operation of Steam Turbine Generators
- 8 Conclusion
Introduction to Steam Turbine Generators
A steam turbine generator is a device that uses steam to rotate turbine blades, which in turn drives an electrical generator to produce electricity. The basic principle behind the operation of steam turbine generators is the conversion of heat energy into mechanical energy, and then into electrical energy.
Steam turbine generators operate based on the principle of converting heat energy from steam into mechanical energy by propelling turbine blades, which are connected to an electrical generator. The high-pressure steam produced by heating water in a boiler is directed onto the turbine blades, causing them to spin rapidly. The spinning motion drives the generator to produce electricity. This process efficiently harnesses the power of steam to generate a significant amount of electrical power, making steam turbine generators a popular choice for power plants worldwide.
Working Principle of Steam Turbine Generators
The process begins with the combustion of fossil fuels such as coal, natural gas, or oil in a boiler to produce high-pressure steam. This high-pressure steam is then directed towards the turbine blades at high velocities. The steam exerts pressure on the turbine blades, causing them to rotate.
As the turbine blades rotate, they turn the shaft connected to the generator, which in turn generates electricity. The electricity produced is then sent to the electrical grid to power homes, businesses, and industries. After passing through the turbine, the steam is cooled and condensed back into water in a separate part of the power plant, known as the condenser. The water is then recycled back to the boiler to be heated again and continue the cycle. This continuous loop of turning turbines with steam to generate electricity is known as the steam turbine power generation process.
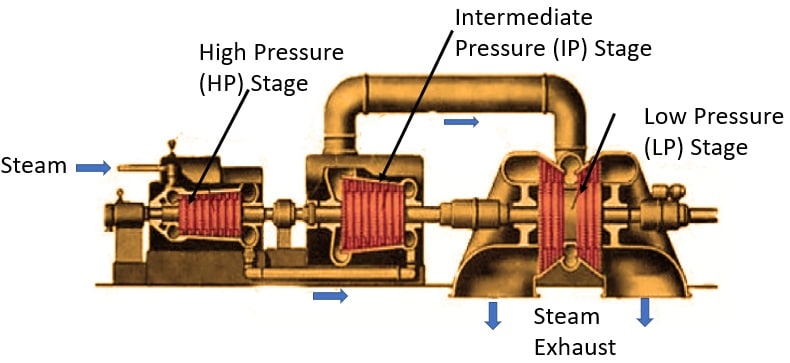
Components of a Steam Turbine Generator
A steam turbine generator consists of several key components, including the turbine rotor, turbine blades, shaft, electrical generator, condenser, and boiler. The turbine rotor is connected to the shaft, which is in turn connected to the electrical generator. As the turbine blades rotate, the generator produces electricity.
Efficiency and Output of Steam Turbine Generators
Steam turbine generators are known for their high efficiency in converting thermal energy into electrical energy. Modern steam turbine generators can achieve efficiencies of up to 45%, making them one of the most efficient ways to generate electricity on a large scale. The output of a steam turbine generator depends on various factors such as the size of the turbine, steam pressure, and temperature.
Higher efficiencies in steam turbine generators are achieved through optimized design and engineering, as well as advanced materials that can withstand high temperatures and pressures. The size of the turbine plays a crucial role in determining the power output, with larger turbines capable of generating more electricity. Steam pressure and temperature also impact the performance of the generator, as higher pressures and temperatures result in more efficient energy conversion. Overall, steam turbine generators are essential components of power plants and play a key role in meeting the energy demands of modern societies.
Types of Steam Turbine Generators
There are several types of steam turbine generators, including condensing and non-condensing turbines. Condensing turbines are used in power plants where steam is condensed back into water after passing through the turbine blades. Non-condensing turbines are used in applications where the steam is released into the atmosphere after passing through the turbine blades.
Applications of Steam Turbine Generators
Steam turbine generators are widely used in power plants, both fossil fuel-fired and nuclear. They are also used in various industries such as oil and gas, chemical, and petrochemicals for power generation. Steam turbine generators are known for their reliability, high efficiency, and long service life, making them a popular choice for electricity generation.
Maintenance and Operation of Steam Turbine Generators
Proper maintenance and operation of steam turbine generators are essential to ensure their optimal performance and longevity. This includes regular inspections, cleaning, lubrication, and monitoring of key parameters such as steam pressure, temperature, and turbine speed. By following a strict maintenance schedule, the efficiency and lifespan of steam turbine generators can be significantly enhanced.
Conclusion
In conclusion, steam turbine generators play a crucial role in the generation of electricity in power plants. By converting thermal energy into mechanical energy and then into electrical energy, these generators provide a reliable and efficient way to meet the growing electricity demand worldwide. Understanding the working principles, components, efficiency, and maintenance of steam turbine generators is essential for ensuring their optimal performance and longevity.



